5 Bioactive Lights for Health: How Red Light Therapy works
In today’s modern world, most of us are missing out on vital light nutrients.
Discover how the five types of bioactive light, especially red light therapy, can boost cellular energy, improve mood, and support overall health by addressing light deficiencies caused by indoor living.

We often overlook a crucial aspect of our well-being: light. Just as we meticulously count calories and track our macronutrients, it's time we start paying attention to our "light diet." Surprising as it may seem, light is not just about illumination—it's a vital nutrient that our bodies crave and require for optimal function.
Imagine this: your cells are like tiny solar-powered engines, constantly hungry for the right kind of light to keep them running smoothly. But here's the kicker—we're not just talking about any light. There are five specific types of bioactive light that play a crucial role in our health:
- Blue light: The master controller of our internal clock
- UV light: Nature's vitamin D synthesizer
- Far-infrared light: The cellular heater
- Red light: The mitochondrial energizer
- Near-infrared (NIR) light: Red light's deeply penetrating cousin
Each of these light types acts like a key, unlocking different biological processes in our bodies.
But here's the problem: our modern lifestyle has us living in a state of "mal-illumination." We're like plants trying to grow in a dark closet, desperately reaching for a light that's not there.

Summary of this article:
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Bioactive Lights in Humans | There are five types of bioactive lights: blue, UV, far-infrared, red, and near-infrared |
| Role of Red Light | Red light stimulates mitochondrial energy production in cells, improving cellular function |
| Near-Infrared Light | Near-infrared light enhances red light's effects, promoting deeper tissue healing and cellular repair |
| Nitric Oxide and Cellular Health | Red and near-infrared light protect cells from nitric oxide damage, ensuring efficient oxygen use |
| Skin and Hair Benefits | Red light therapy improves skin health, stimulates collagen production, and aids in hair growth |
| Inflammation and Pain Relief | The therapy reduces inflammation and pain by promoting cellular recovery and reducing oxidative stress |
| Muscle Recovery | Red light aids in muscle recovery by boosting ATP production and reducing recovery time |
| Frequency and Safety | Red light therapy is safe for daily use with little to no side effects |
| Mitochondrial Health | The therapy enhances mitochondrial efficiency, increasing energy (ATP) for optimal cellular functions |
| Home Use of Red Light Therapy | Red light therapy is available through devices for convenient at-home use |
Understanding Light as a Nutrient
The concept of bioactive light
When we think of nutrients, our minds typically jump to vitamins, minerals, and macronutrients like proteins and carbohydrates. However, there's another essential nutrient that we often overlook: light. Just as our bodies require specific chemical compounds to function optimally, they also need particular wavelengths of light to thrive.
Bioactive light refers to specific types of light that have a biological effect on our bodies. These wavelengths of light aren't just passive illumination; they actively influence our cellular processes, hormonal balance, and overall health. The concept of bioactive light challenges us to reconsider our relationship with light and its role in our well-being.
How light affects cellular function
At the cellular level, bioactive light acts as a catalyst for numerous biological processes. Different wavelengths of light can:
- Stimulate mitochondria, our cellular powerhouses, to produce more energy
- Influence the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy currency of cells
- Affect the release of nitric oxide, a molecule involved in various physiological processes
- Modulate inflammation and oxidative stress
- Influence gene expression and protein synthesis
These effects aren't limited to our skin cells. Thanks to the penetrative abilities of certain wavelengths, like red and near-infrared light, bioactive light can influence tissues deep within our bodies, including muscles, bones, and even brain tissue.
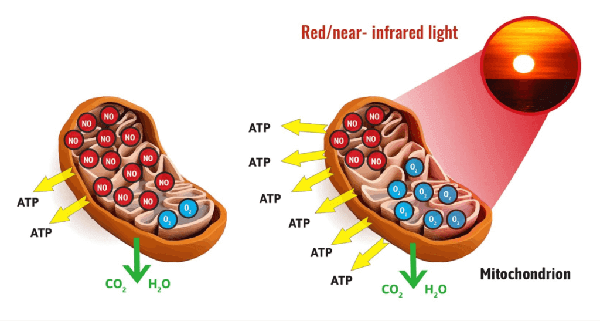
The importance of light exposure for overall health
The impact of bioactive light extends far beyond cellular function. Proper light exposure plays a crucial role in:
- Regulating our circadian rhythms and sleep-wake cycles
- Synthesizing essential vitamins, such as vitamin D
- Modulating our mood and cognitive function
- Supporting our immune system
- Promoting wound healing and tissue repair
Unfortunately, our modern lifestyle often leads to what researchers call "mal-illumination" – a state of light deficiency or imbalance. Just as malnutrition can lead to various health issues, mal-illumination can contribute to a wide range of health problems, from sleep disorders to chronic diseases.
"LLLT/PBM (photobiomodulation) is more than an alternative kind of medical treatment; it is a whole new method to control cellular processes and modulate living organisms by precise alterations in the chemistry of biomolecules." - Michael Hamblin
This quote from Michael Hamblin, a leading researcher in the field, underscores the profound potential of light as a tool for health and healing. By understanding and harnessing the power of bioactive light, we open up new possibilities for supporting our health and well-being in the modern world.
In the following sections, we'll explore the five specific types of bioactive light that are crucial for human health, delving into their unique properties and effects on our bodies. This journey will not only illuminate the importance of light as a nutrient but also provide practical insights into how we can optimize our light exposure for better health.
The Five Bioactive Light Types
Understanding the different types of bioactive light is crucial for appreciating their diverse effects on our health. Let's explore each of these light types and their unique roles in our biology.
1- Blue light and circadian rhythms
Blue light, typically with wavelengths between 450-495 nanometers, plays a pivotal role in regulating our circadian rhythms - our internal 24-hour biological clock.
Primary source: Sunlight, particularly during daytime hours
Biological effects:
- Suppresses melatonin production
- Increases alertness and cognitive function
- Regulates sleep-wake cycles
Did you know? While natural blue light from the sun is beneficial during the day, excessive exposure to artificial blue light from screens at night can disrupt our sleep patterns.
2- UV light and vitamin D synthesis
Ultraviolet (UV) light, specifically UVB with wavelengths between 280-315 nanometers, is essential for vitamin D production in our skin.
Primary source: Sunlight
Biological effects:
- Triggers vitamin D synthesis
- Supports bone health
- Modulates immune function
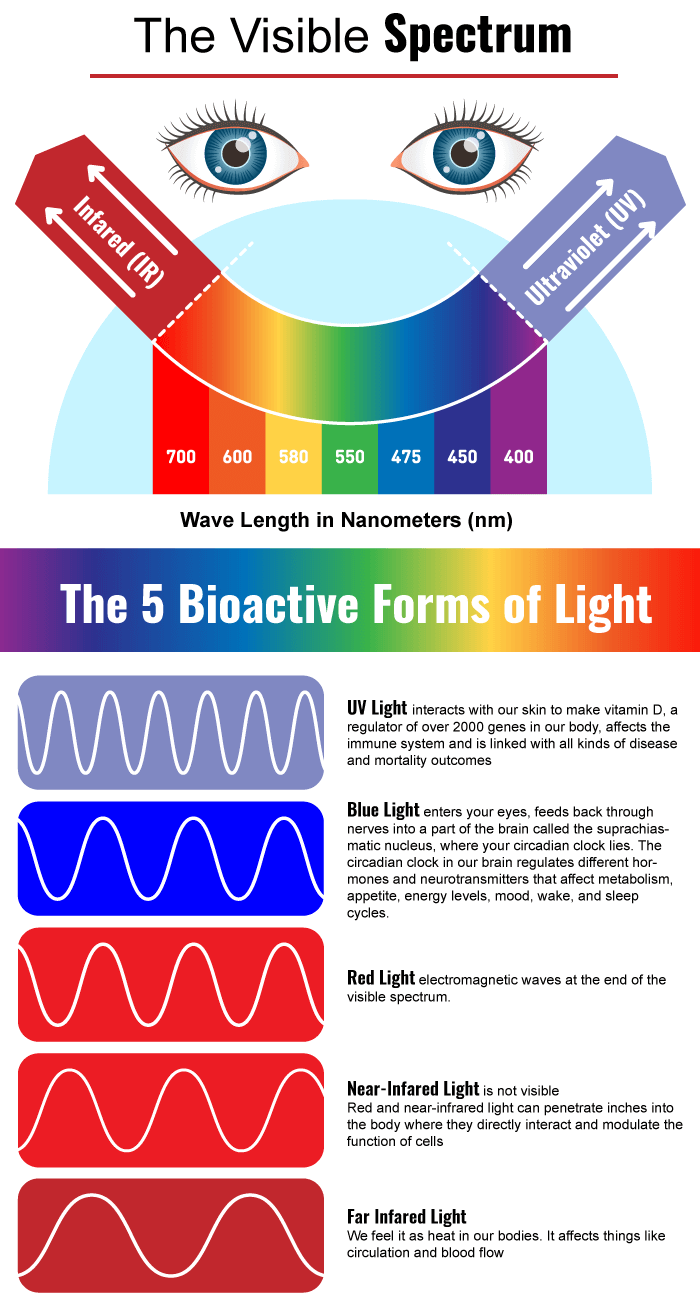
3- Far-infrared light and cellular heating
Far-infrared light, with wavelengths between 3,000-100,000 nanometers, is felt as heat and can penetrate deep into our tissues.
Primary source: Sun's heat, infrared saunas
Biological effects:
- Increases cellular temperature
- Enhances circulation
- Promotes detoxification through sweating
4- Red light and cellular energy production
Red light, with wavelengths between 620-750 nanometers, has gained significant attention for its ability to boost cellular energy production.
Primary source: Sunlight, specialized red light therapy devices
Biological effects:
- Stimulates mitochondrial function
- Increases ATP production
- Promotes collagen synthesis
- Reduces inflammation
5- Near-infrared light and its similarities to red light
Near-infrared (NIR) light, with wavelengths between 750-1400 nanometers, shares many benefits with red light but can penetrate even deeper into our tissues.
Primary source: Sunlight, specialized NIR therapy devices
Biological effects:
- Enhances mitochondrial function
- Supports cellular repair and regeneration
- Reduces oxidative stress
- Promotes wound healing
Each of these light types acts as a unique "nutrient" for our bodies, influencing various physiological processes. In our modern indoor-centric lifestyles, we often don't get enough exposure to these beneficial light wavelengths, leading to what researchers term "mal-illumination."
Understanding these five bioactive light types is the first step towards optimizing our "light diet." By ensuring we get the right types of light at the right times, we can support our body's natural rhythms and cellular functions, potentially leading to improved overall health and well-being.
The Modern Light Deficiency Problem
As we've evolved into a predominantly indoor species, we've inadvertently created a new health challenge: widespread light deficiency. This shift in our light exposure patterns has far-reaching consequences for our health and well-being.
Indoor living and reduced sun exposure
Our ancestors spent most of their waking hours outdoors, bathed in natural sunlight. In stark contrast, modern humans often find themselves in a very different light environment:
- 🏢 The average American spends about 93% of their time indoors[1]
- 💻 Many of us work under artificial lighting for 8+ hours a day
- 📱 We expose ourselves to blue light from screens well into the night
This dramatic shift has resulted in a significant reduction in our exposure to the full spectrum of natural light, particularly the beneficial red and near-infrared wavelengths.
The concept of mal-illumination
Just as malnutrition refers to a diet lacking essential nutrients, "mal-illumination" describes a state of chronic deficiency in healthful light exposure. This concept, coined by Dr. John Ott, highlights the importance of light as a nutrient for our bodies. Mal-illumination can manifest in various ways:
- Insufficient exposure to natural sunlight
- Overexposure to artificial light, especially at night
- Imbalance in the types of light we receive throughout the day
"The vast majority of people living in the modern world are suffering from chronic mal-illumination and don't even realize it." This state of light deficiency can have widespread effects on our health, influencing everything from our sleep quality to our immune function.
Comparing outdoor vs. indoor light exposure
To truly grasp the extent of our light deficiency, consider these stark comparisons:
| Light Environment | Typical Light Intensity (lux) |
|---|---|
| Bright summer day outdoors | 50,000 - 100,000 |
| Overcast day outdoors | 1,000 - 5,000 |
| Typical office lighting | 300 - 500 |
| Living room in the evening | 50 - 200 |
The difference is staggering - we're often exposed to light levels indoors that are **100 to 1000 times lower** than what we would experience outdoors! But it's not just about intensity. Indoor lighting often lacks the full spectrum of light wavelengths found in natural sunlight, particularly in the red and near-infrared ranges. This means that even if we're in well-lit indoor environments, we're still likely deficient in certain beneficial light wavelengths.
Understanding this modern light deficiency problem is crucial for recognizing the importance of intentional, healthful light exposure in our daily lives. In the next section, we'll explore the potential health consequences of this light deficiency and why addressing it is so important for our overall health.
Scientific studies:

Health Consequences of Light Deficiency
The impact of chronic light deficiency extends far beyond just feeling a bit under the weather. As we uncover more about the intricate relationship between light and human biology, it becomes clear that mal-illumination can have profound effects on our health.
Vitamin D deficiency and related health issues
One of the most well-known consequences of inadequate sunlight exposure is vitamin D deficiency. This "sunshine vitamin" plays a crucial role in numerous bodily functions:
- 🦴 Bone health and calcium absorption
- 🛡️ Immune system regulation
- 🧠 Neurotransmitter synthesis
- 💪 Muscle function
Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to a variety of health issues:
- Osteoporosis and increased fracture risk
- Increased susceptibility to infections
- Higher risk of autoimmune diseases
- Mood disorders, including depression
Startling statistic: It's estimated that over 1 billion people worldwide have vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency[2].
Circadian rhythm disruption and its effects
Our bodies rely on consistent light cues to maintain our circadian rhythms. Disruption of these rhythms due to irregular light exposure can lead to:
- Sleep disorders
- Hormonal imbalances
- Metabolic issues
- Mood disorders
- Cognitive impairment
Increased risk of chronic diseases
Research has shown that chronic light deficiency and circadian rhythm disruption are associated with an increased risk of several serious health conditions:
- Cancer:Studies have linked low sun exposure to increased risk of various cancers, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer[4].
- Cardiovascular disease: Inadequate sunlight exposure has been associated with higher blood pressure and increased risk of heart disease[5].
- Diabetes and obesity: Disrupted circadian rhythms can affect metabolism and insulin sensitivity, potentially contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes and obesity[6].
- Neurodegenerative diseases: There's emerging evidence linking chronic light deficiency to an increased risk of conditions like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease[7].
The surprising link between low sun exposure and mortality
Perhaps most alarming is the potential link between insufficient sun exposure and overall mortality risk. A Swedish study spanning 20 years and involving nearly 30,000 women found a startling correlation: Women with the lowest sun exposure had a twofold higher rate of death compared to the women with the most sun exposure.
This finding suggests that the health impacts of chronic light deficiency may be even more far-reaching than we currently understand.
| Health Issue | Potential Impact of Light Deficiency |
|---|---|
| Vitamin D levels | Significant decrease, leading to various health risks |
| Sleep quality | Disrupted sleep patterns, insomnia |
| Mood | Increased risk of depression, especially seasonal affective disorder |
| Metabolic health | Potential increase in obesity and diabetes risk |
| Cardiovascular health | Possible increase in blood pressure and heart disease risk |
| Cancer risk | Potential increase for certain types of cancer |
Understanding these potential health consequences underscores the importance of addressing our modern light deficiency problem.
Scientific studies:
[2]: Holick, M. F. (2007). Vitamin D deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine, 357(3), 266-281.
You can fin the next part of this article here:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is red light therapy?
Red light therapy uses specific wavelengths of light to stimulate cellular function, primarily through the mitochondria, to promote healing and energy production.
How does red light therapy work?
Red light is absorbed by chromophores in cells, initiating a biochemical response that boosts ATP production, improving cellular function and overall health.
What are the benefits of red light therapy?
Red light therapy can improve skin health, reduce inflammation, promote hair growth, and enhance muscle recovery.
Can red light therapy be used daily?
Yes, red light therapy is safe for daily use and has minimal to no side effects when used appropriately.
How deep does red light penetrate the skin?
Red light penetrates the skin's surface, while near-infrared light reaches deeper tissues, targeting areas like mitochondria for enhanced healing.
Does red light therapy help with inflammation?
Yes, red light therapy is known to reduce inflammation by promoting cellular recovery and decreasing oxidative stress.
Is red light therapy safe for all skin types?
Yes, it is non-invasive and safe for all skin types, offering benefits like improved skin tone and texture without causing damage.
Can red light therapy aid in muscle recovery?
Yes, it accelerates muscle recovery by boosting ATP production, reducing inflammation, and decreasing recovery time.
What wavelengths are used in red light therapy?
Red light therapy typically uses wavelengths between 630nm-660nm for visible red light and 850nm for near-infrared light.
Can red light therapy be done at home?
Yes, many devices are available for at-home use, allowing people to experience the benefits of red light therapy conveniently.
















